ESG stands for environmental, social, and governance. It’s a set of standards that investors use to screen investments and assess a company’s impact on society. In the past, ESG was considered little more than nice-to-have information for investors—ESG provided some context regarding a company’s business practices but didn’t factor heavily into investment decisions.
Now, ESG is becoming increasingly important for investors, including both individuals and institutions. With this shift, companies need to pay more attention to their ESG rating. By better understanding ESG and its use, you can ensure your company can be prepared.
What Is an ESG Rating?
A company’s ESG rating is a measure of its environmental, social, and governance performance. It’s a way for investors to assess a company’s impact on society and the environment. There is a great deal of criteria that goes into a company’s ESG rating. Evaluators consider the following.
Environmental Impact
This includes a company’s carbon footprint, its use of renewable energy, its waste management practices, and its water usage. When being assessed for its environmental impact, a company can demonstrate environmental leadership and the ongoing impact of sustainability trends by setting goals to reduce its carbon footprint or by investing in renewable energy. Any progress a company makes toward these goals can help to improve its ESG rating. This must be demonstrated with reliable, consistent and verified data.
Social Impact

This includes a company’s treatment of its employees, its diversity and inclusion practices, its supply chain management, and its customer service. When attempting to better understand how an organization is impacting society, it’s important to consider how it treats its stakeholders. This includes its employees, its customers, and its suppliers. This can be difficult to measure, but companies can provide evidence of their social impact by sharing data on employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction, or supplier diversity. The more data a company can share, the better its social impact score will be.
Governance Impacts
This includes a company’s board diversity, executive compensation, shareholder rights, and disclosure policies. A company’s governance score will be based on how well it adheres to best practices in these areas. For example, a company that has a diverse board of directors or that discloses its executive compensation will have a higher governance score than a company that does not.
Companies are assessed on their environmental, social, and governance performance using a variety of data sources. This can include publicly available data, such as a company’s financial filings. Evaluators also use data from third-party organizations, such as environmental impact reports.
Why ESG Has Become Important
There are a few factors driving the increased importance of ESG that investors should be aware of.
Sustainability-Focused Investing
The first factor is the rise of sustainability-focused investing. Sustainability-focused investors are those who consider environmental, social, and governance factors when making investment decisions. This type of investing is often referred to as impact investing. Impact investors seek to invest in companies that are having a positive impact on society and the environment. This can include investing in renewable energy, supporting companies that are working to reduce their carbon footprint, or investing in companies that are promoting social good.
The growth of sustainability-focused investing has been driven in part by an increase in awareness of the need for climate action. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (IPCC) report, which was released in October 2018, found that we have approximately 12 years to take action to avoid catastrophic climate change. This report has helped to raise awareness of the need for climate action and motivated people to invest in companies that are working to address climate change.
Responsible Investing
Another factor driving the shift to ESG is the growth of responsible investing. Responsible investing is an investment approach that-much like sustainability-focused investing—considers environmental, social, and governance factors that match the investor’s values. This type of investing has been growing in popularity in recent years as more investors are looking to put their money into companies that are aligned with their values.
The rise of responsible investing has been driven in part by the growth of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and index funds that focus on responsible investing. These types of investment products make it easier for investors to put their money into companies that are aligned with their values. For example, there are ETFs that focus on companies that are working to reduce their carbon footprint and others focused on companies that are promoting social good.
How Do I Find a Company’s ESG Rating?
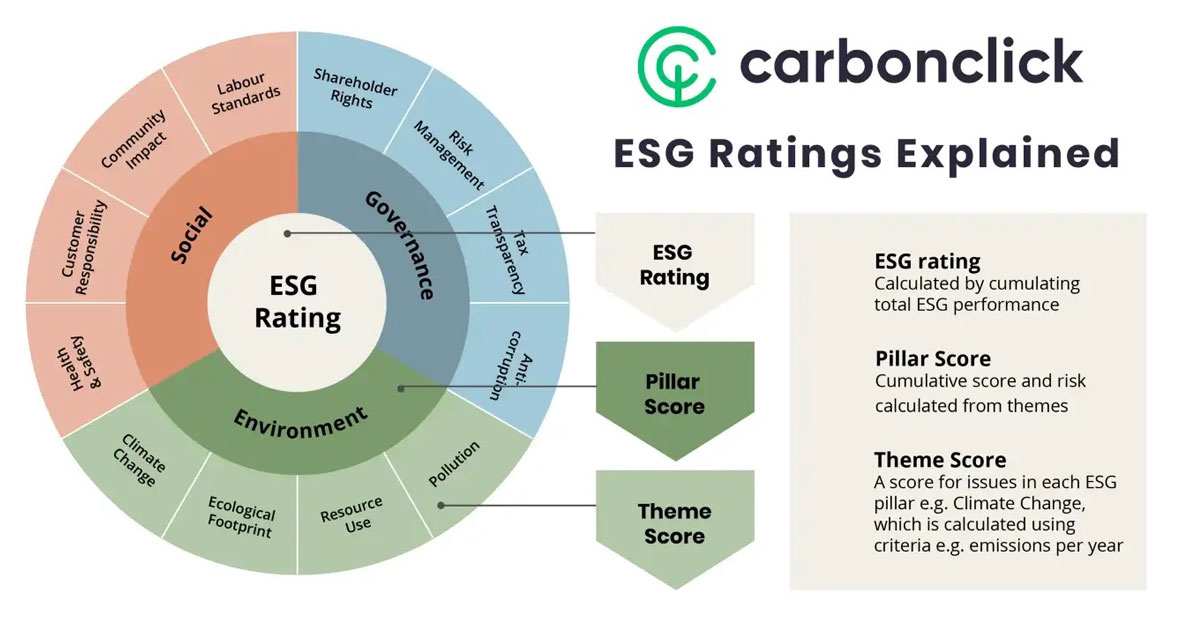
Caption: Graphic Courtesy CarboncClick
There are a few different ways to find a company’s ESG rating. The first is to search for the company on an ESG rating platform, such as Sustainalytics or MSCI. These platforms provide detailed ESG reports for most companies.
Another way to find a company’s ESG rating is to look at the investment products that hold the stock. For example, if you’re looking at an ETF that focuses on responsible investing, the fund’s website should list the companies that are included in the fund and their respective ESG ratings. This can be a good way to get a quick overview of a company’s ESG rating and give you a sense of whether the company is aligned with your values.
What Is the Impact of a Company’s ESG Rating?
A company’s ESG rating can have a significant impact on its business for many reasons. affecting everything from its ability to raise capital to the type of talent it attracts.
Cost of Capital
ESG ratings can affect the cost of capital. Companies with higher ESG ratings tend to have lower borrowing costs because investors view them as being less risky. This is because companies with strong ESG ratings are typically better managed and have a smaller environmental footprint. As a result, they are less likely to be impacted by regulation or public scrutiny.
Ability to Attract and Retain Talent
A company’s ESG rating can also affect its ability to attract and retain talent. Employees, especially those in the millennial and Gen Z generations, are increasingly interested in working for companies that have a positive social and environmental impact. If they witness firsthand that a company is not living up to its ESG commitments, they are likely to leave. If the company has a poor rating or experiences a PR nightmare that affects its reputation, it will have a hard time recruiting top talent who deeply care about these issues.
Share Prices
In addition, a company’s ESG rating can impact its share price. Investors are increasingly interested in responsible investing, and they are more likely to invest in companies with high ESG ratings. Most investors state that this is because they believe these companies will outperform their peers over the long term.
Because the demand for these offerings is high, the share prices of companies with strong ESG ratings tend to be more resilient during market downturns. There is no sign that the values-based investing movement is slowing down, which means that a company’s ESG rating will likely only become more important in the years to come.
What Is a Good ESG Score?
There is no easy answer to this question because it depends on the industry and even the specific company. For example, a utility company that has a low carbon footprint would have a good ESG score, but a clothing company that uses sustainable materials would have an even better score because ratings depend on context. The overall point system used by the various ESG rating platforms can also vary but is typically on a scale of 0 to 100, with 100 being the highest possible score.
An indication of a “good” ESG score is typically a company that ranks in the top tier of its industry, usually with a 70 or higher. Any score in the 50s is considered average, while a score in the 40s or below is considered poor.
For that reason, a company’s ESG score can be a good way to compare it to its peers. If a company has a score that is significantly lower than its peers, regardless of its current ESG ranking, it may be a red flag. A comparatively lower ESG score could be an indication that the company is not doing enough to address environmental and social issues.
It’s also worth noting that a company’s ESG score can change over time, as ESG rating agencies are constantly collecting new data and revising their methodologies. Even if a company had a good score last year, it’s possible that its score could drop this year if the company is not keeping up with its peers.
The Bottom Line: Your ESG Rating Matters

A company’s ESG rating is becoming increasingly important as more and more investors focus on responsible investing. In addition, the general public has become more aware of environmental and social issues. As a result, a company’s ESG rating can affect its cost of capital, ability to attract talent, and share price.
The shift in mindset towards ESG investing appears to be here to stay, which means that companies need to start paying attention to their ratings. Today, an ESG score can indicate how a company’s operations stack up and align to these ideals that the public is demanding. The Boon Room educates the public on sustainability through hemp and advocating for it’s continued uses. Subscribe to our newsletter for regular tips on sustainability

I’m a kid at heart disguised as a cannabis researcher and business owner. I’ve always enjoyed providing insight in the form of reviews (anime, video games, etc.) So, when the cannabis industry took off, it sparked my interest in researching, reviewing, and chronicling all things within. When I’m not researching, I’m spending time with my family, riding my motorcycle, and finding new entrepreneurial pursuits.

